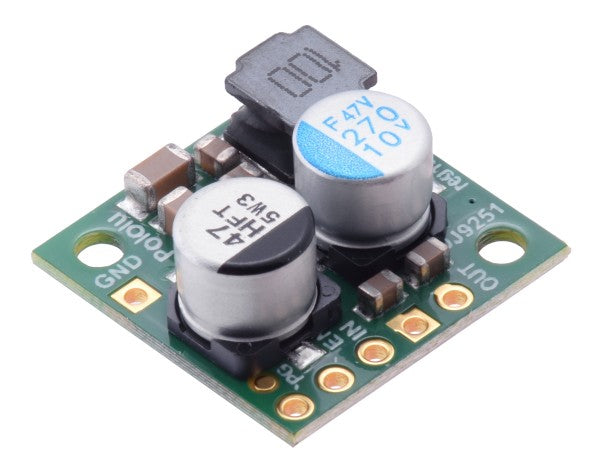
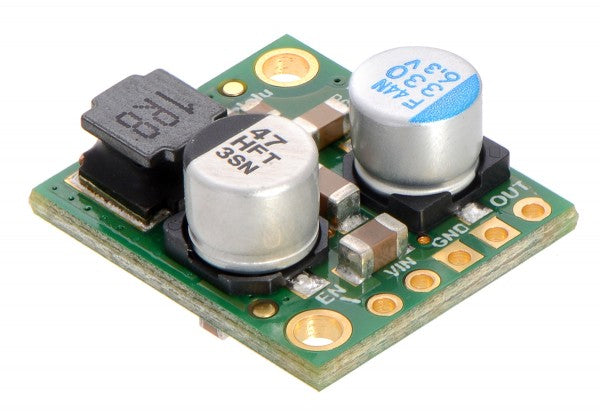
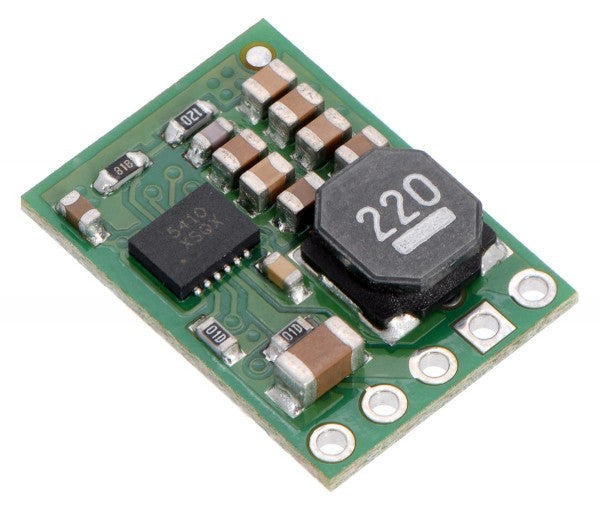
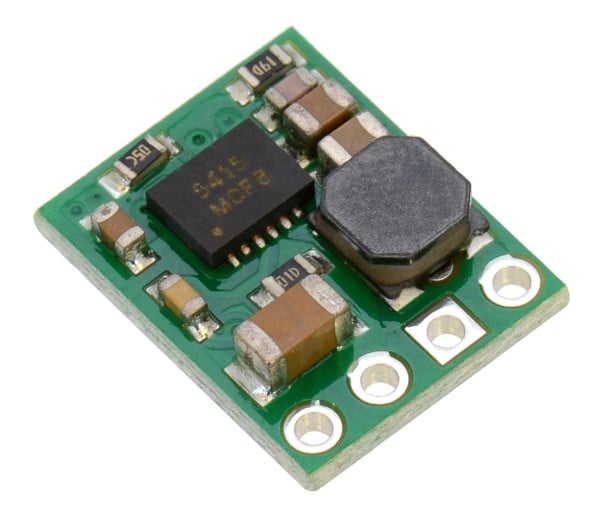
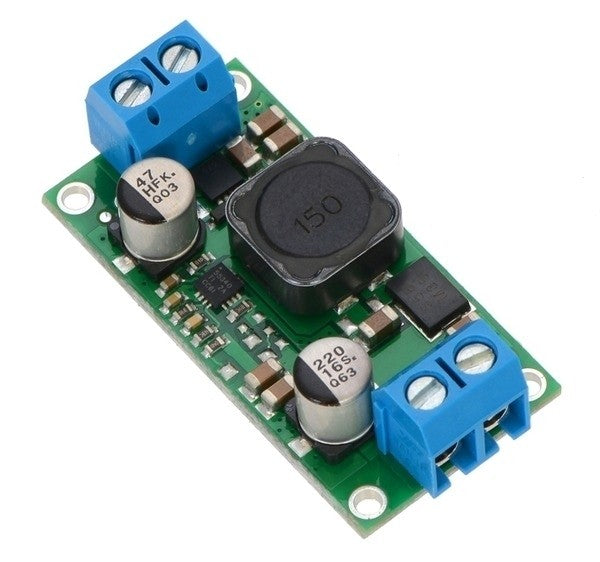
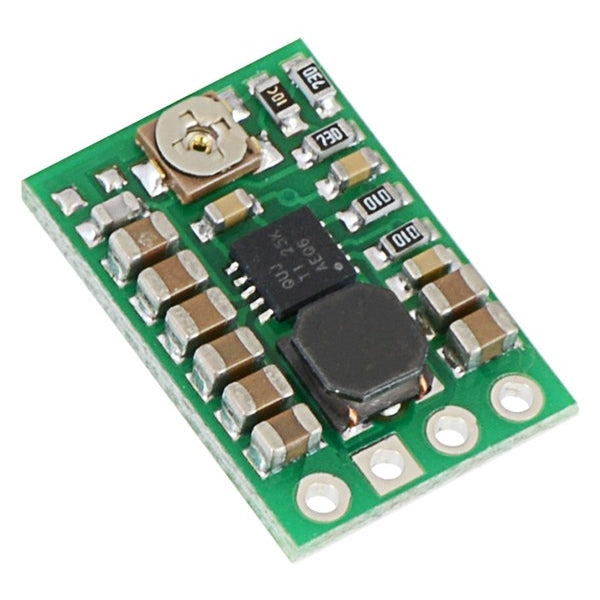
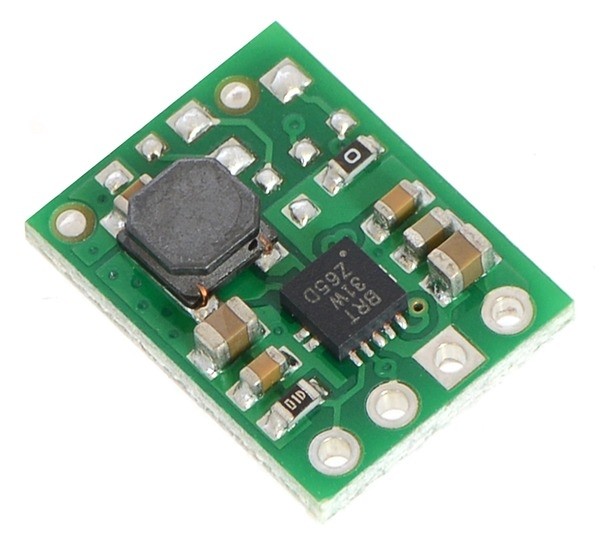
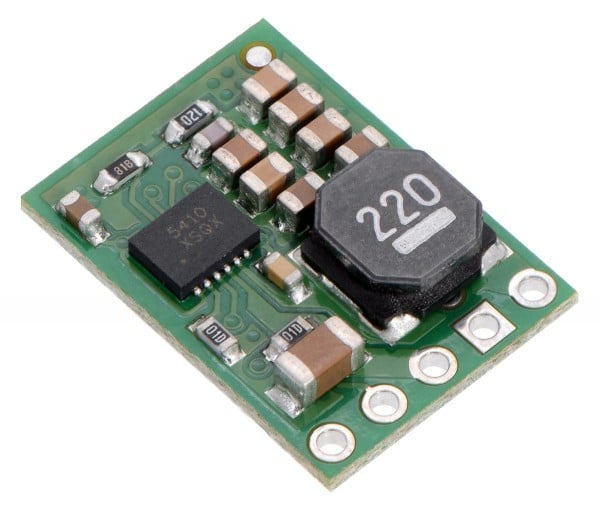
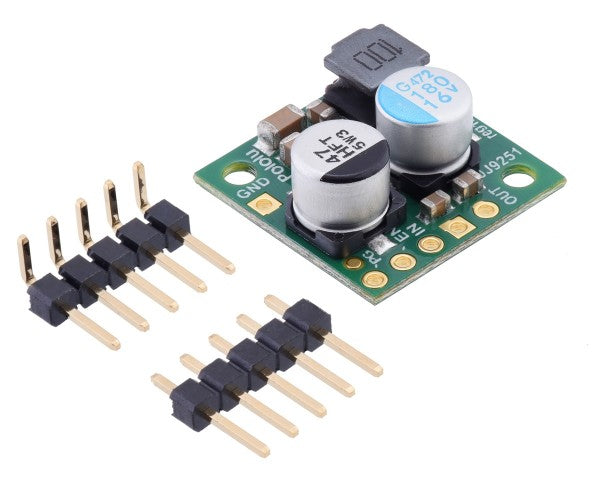
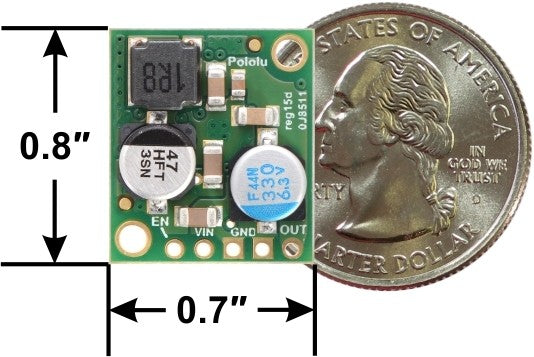
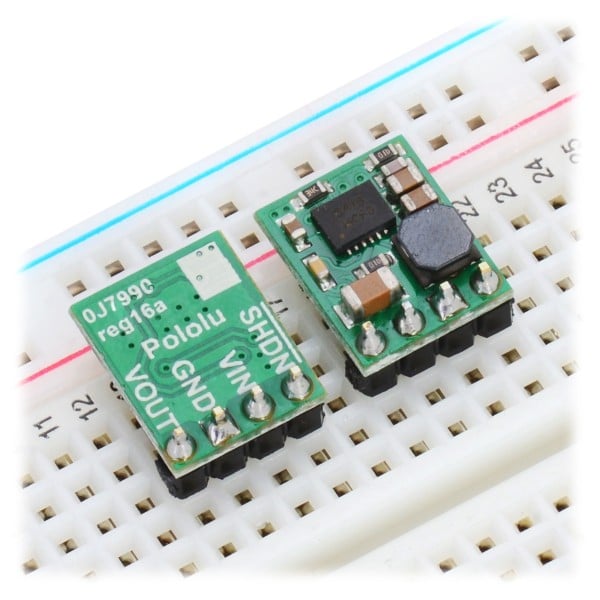
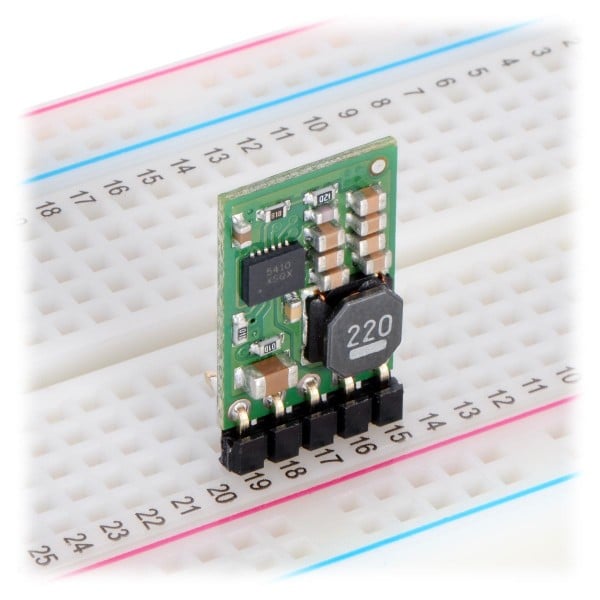
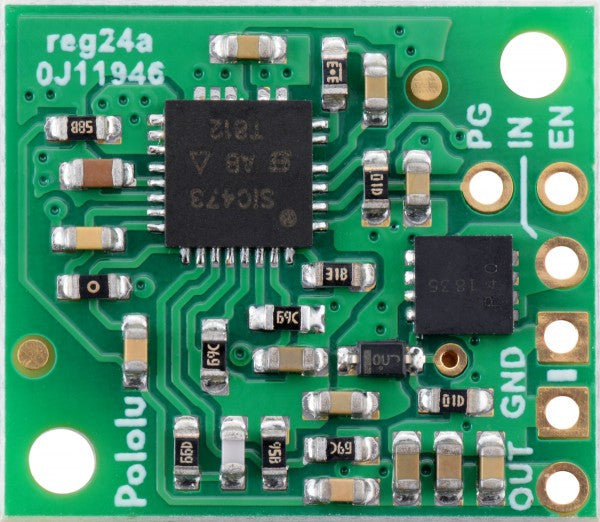
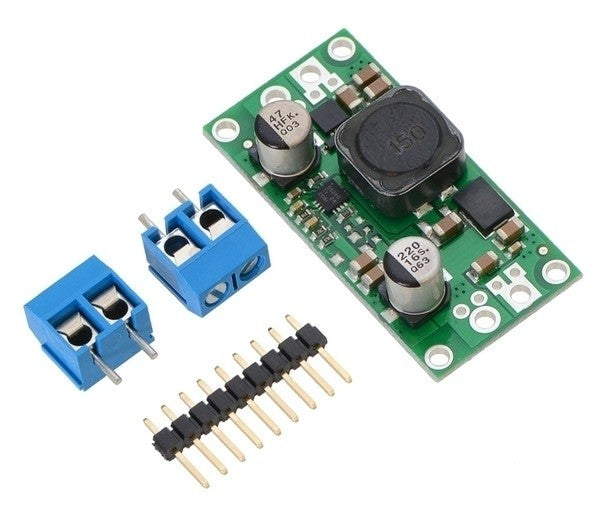
Voltage regulators as a central component in electronics
All kinds of electronic devices require a constant operating voltage at a fixed level. Often, the input voltage from power supplies, batteries, and the like exceeds this value, making a reduction in voltage essential: this is achieved by step-down voltage regulators. They reduce the input voltage to the desired output voltage level. Is the input voltage too low? Then a step-up voltage regulator can help.
These two basic types, along with buck-boost voltage regulators and shunt regulators as two variations, are available here in the shop in numerous versions. Whether you're a tradesperson, industrial company, or an ambitious electronics hobbyist: equip yourself here with high-quality voltage regulators!
These two basic types, along with buck-boost voltage regulators and shunt regulators as two variations, are available here in the shop in numerous versions. Whether you're a tradesperson, industrial company, or an ambitious electronics hobbyist: equip yourself here with high-quality voltage regulators!
Different types of voltage regulators
If your project requires voltage regulation , the first question is what specific function it needs to perform. Choose from the following types of voltage regulators:
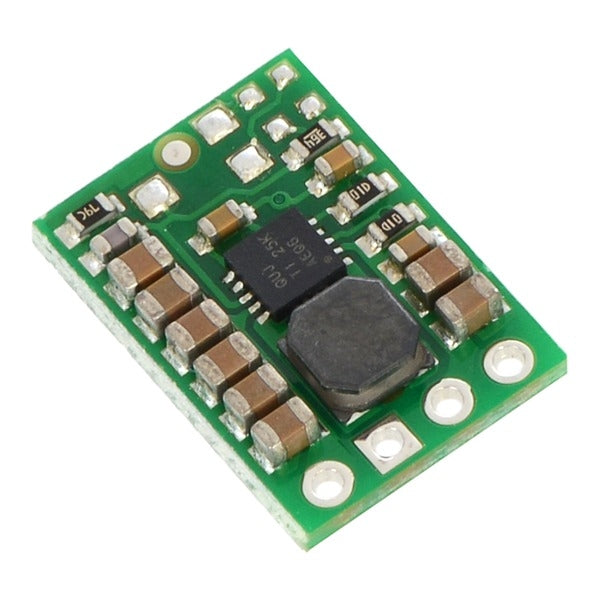
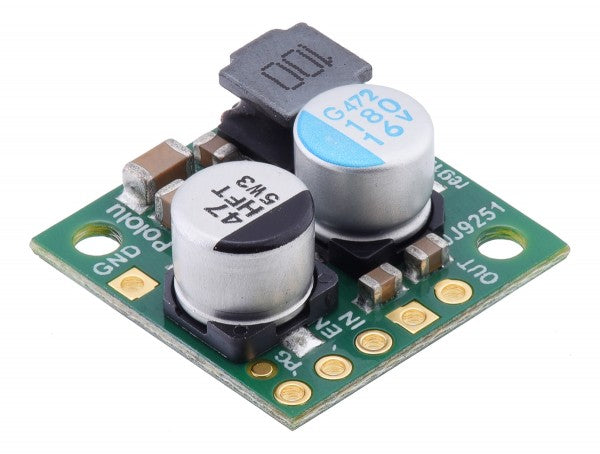
The step-down voltage regulator
This type is a buck converter that reduces a high input voltage to a lower output voltage. A key consideration is the degree of voltage reduction the regulator can achieve. What maximum input voltage does it reduce to which level?
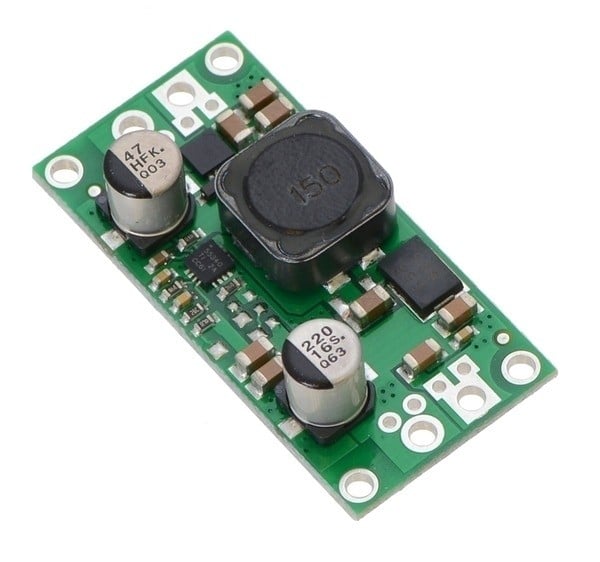
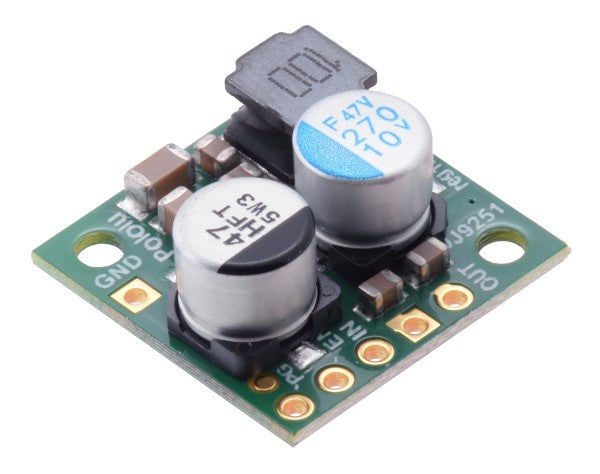
The step-up voltage regulator
The boost converter increases a low input voltage to a higher level. Again, it's important to note the minimum and maximum values for input and output voltage.
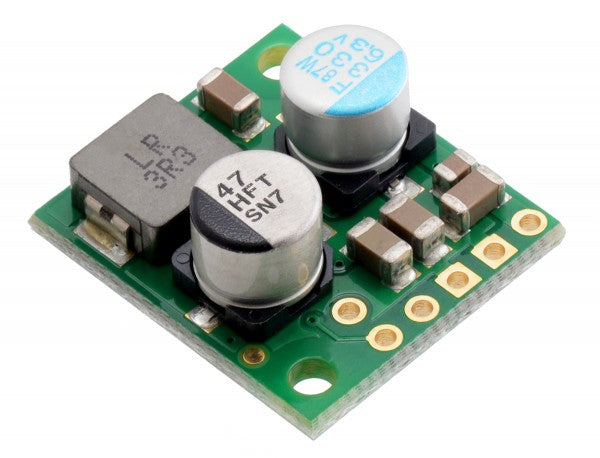
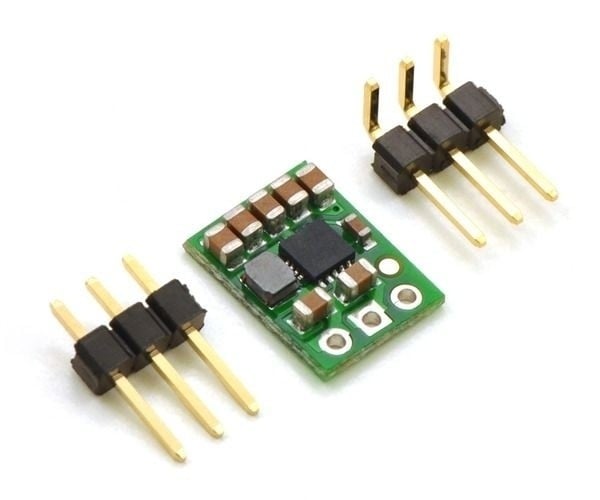
The buck-boost voltage regulator
A buck-boost converter offers the flexibility to handle both functions. These adaptable buck-boost regulators ensure a constant operating voltage in dynamic environments.
The shunt regulator
This is a classic parallel regulator, designed for low-power applications and only capable of reducing voltage—unlike switching regulators. This type requires current limiting, which is often implemented using a series resistor. One advantage is the low cost; disadvantages include limited applications and lower efficiency.
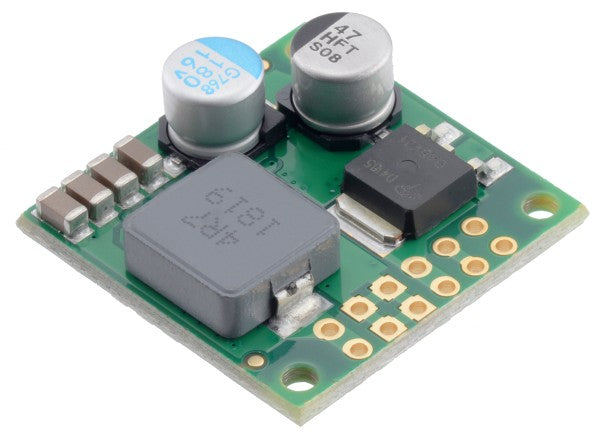
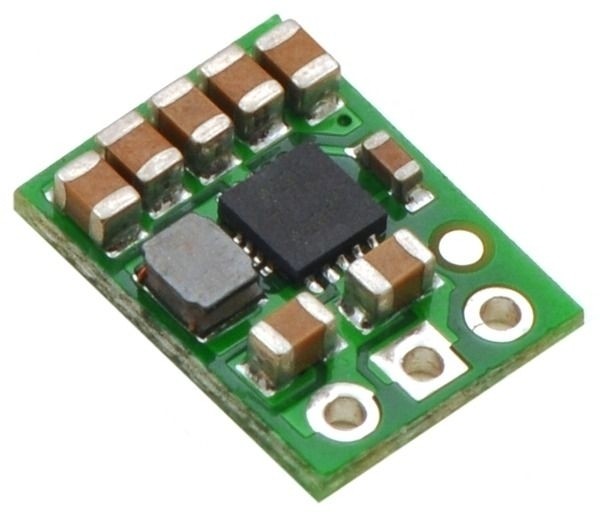
Innovative switching regulators instead of linear regulators
In practice, efficient switching regulators have become the standard, while linear regulators like shunt regulators now play only a minor role. Whether step-down voltage regulators or buck-boost regulators: modern switching regulators perform reliably—with high efficiency!
Advantages of switching regulators at a glance:
- high efficiency
- excellent thermal performance
- wide voltage range supported
- designed for higher currents
Note that switching regulators often require additional components such as capacitors. Consult with your electrical engineering experts for advice!