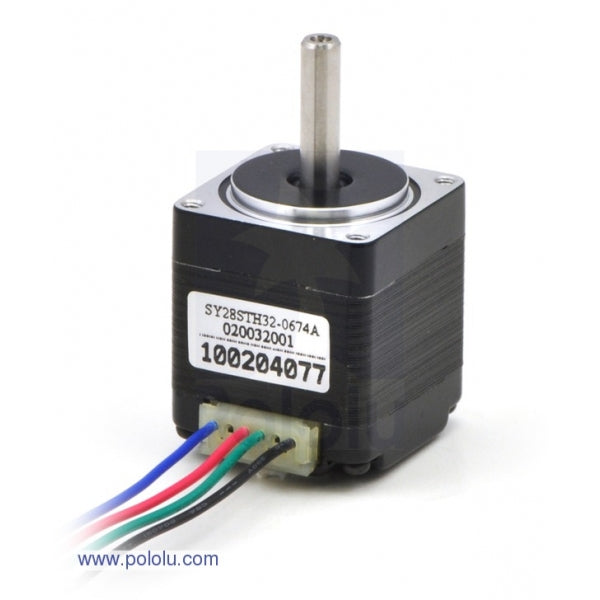
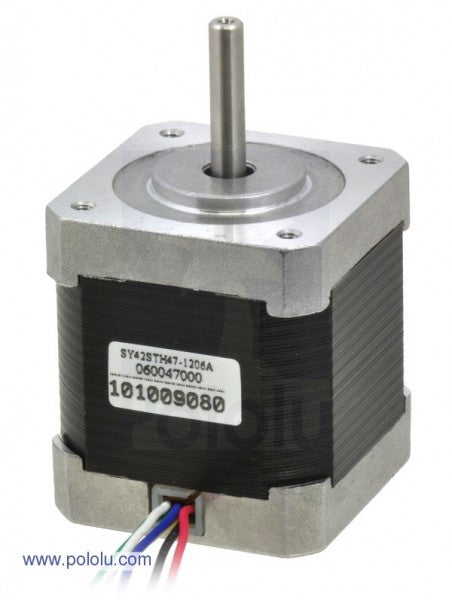
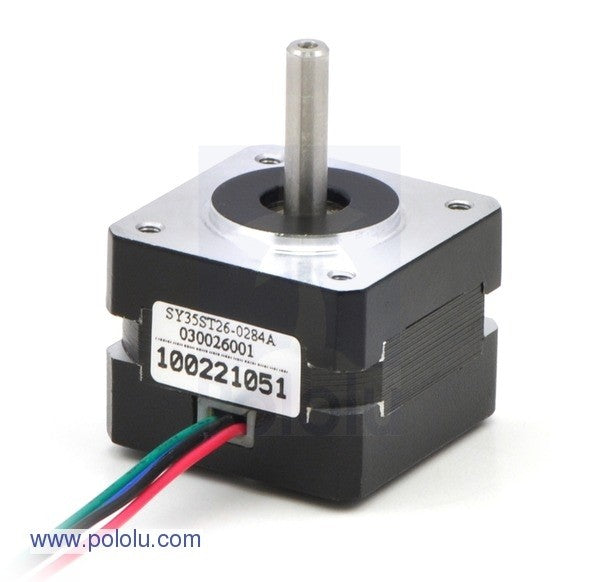
Precise control and exact positioning: the strengths of stepper motors
The main feature of stepper motors is that they can be positioned exactly. The rotor of these motors moves in small steps, measured as an angle in degrees. This allows the component attached to the motor to be aligned exactly, and the speed of the movements can also be easily controlled.
This special mode of operation is important for printers and 3D printers, for example. These devices are based on exact positioning, otherwise the print will be unsuccessful. A stepper motor also provides valuable services for valves and flaps when it comes to precisely positioning these components at a specific angle. Dozens of stepper motors can be found in many motor vehicles, moving valves in the air conditioning and ventilation system, among other things.
Other typical applications include:
- Motors in robots
- Toys with stepper motors
- Stepper motors in machine tools
Precise control is required in all these applications – the stepper motor is often controlled using an Arduino controller.
How it works: This is how a stepper motor converts pulses into precise movements
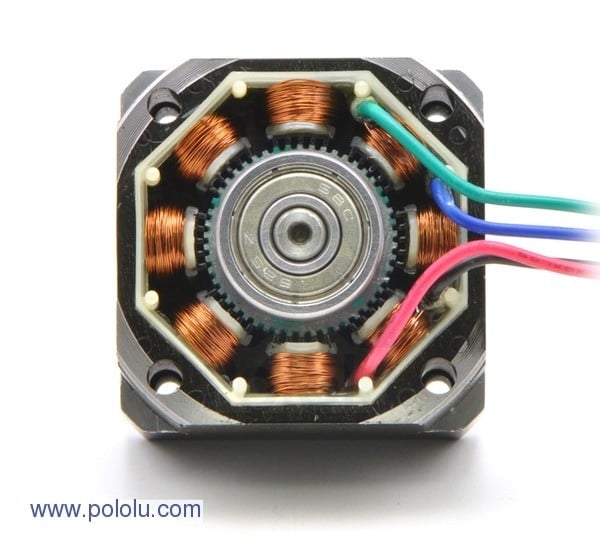
The design of a stepper motor differs from that of other DC motors in that coils are only located in the fixed stator. The moving rotor has no windings. These coils generate a magnetic field that moves the rotor in the desired direction. The motor controls the position by selectively switching individual windings on and off.
It is worth comparing stepper motors with servo motors at this point: both types of motor guarantee precise positioning, but there is a significant difference between them. Servo motors have a sensor that reports the current position. Stepper motors manage without this component and still function reliably. At the same time, the simple design ensures a low purchase price.
Controlling stepper motors: an overview of options
Stepper motors require a power supply and a controller. A driver board controls the stepper motor and ensures that it performs the desired steps. Combinations of Arduino and stepper motor are common. The Arduino controller acts as a control element, while the stepper motor acts as an executing element. The key factor here is controlling the current flow – specifically switching the windings on and off at the stator. However, there are also alternatives to stepper motors with Arduino, including stepper motors with Raspberry Pi.
Stepper motor for your project: what to consider
Choosing the right stepper motor depends on several factors that affect precision, performance and controllability. In addition to the fundamental decision between a unipolar and a bipolar stepper motor, the number of phases, the step angle, the torque, the rated voltage and compatibility also play an important role.
Unipolar or bipolar – which type is right for you?
When you buy a stepper motor, you should first decide whether a unipolar or bipolar motor is better suited for your application. Unipolar motors are easier to control because they have a centre tap in the windings and do not require a complex H-bridge circuit. However, they offer a lower torque because only one half of the winding is ever active. Bipolar motors use the entire winding, which gives them more torque and higher efficiency. However, they require more complex control electronics.
Number of phases – influence on smooth running and precision
An important factor is the number of phases of a stepper motor. It determines how many pairs of coils are active in the motor and thus directly influences the smoothness and precision of the movement. Two-phase steppers are the most common, while multi-phase models enable an even smoother rotation.
Step angle – accuracy and microstepping
The step angle is of particular importance. This value is directly related to the number of steps per revolution. Many stepper motors achieve 200 steps per revolution, resulting in a step angle of 1.8 degrees. With so-called microstepping, which is implemented using additional electronic solutions, the step angle can be further reduced, enabling even more precise positioning.
Torque – force and load capacity of the motor
Torque is crucial for the performance of a stepper motor. It indicates how much force the motor can apply to move or hold a load. The higher the torque, the better the motor is suited for applications with greater resistance or heavy loads. Choosing the appropriate torque depends heavily on the intended use and the mechanical load.
Nominal voltage – power supply and efficiency
The nominal voltage of the motor is equally important. It influences the current behaviour and power consumption of the motor in conjunction with the driver. While a higher voltage often results in better high-speed properties, it must be combined with the appropriate current limiting to prevent overheating and damage.
Compatibility – control with Arduino and Raspberry Pi
When comparing motors, also check which controllers the respective version is compatible with. Will your stepper motor work with the Arduino library? Can it be controlled with Raspberry Pi? You will find answers to these and other questions in the individual product descriptions of the brand models from Pololu and Co.
Find the right stepper motor for your project now
A precisely tuned motor ensures reliable and efficient movement in your application, be it in robotics, automation or industry.
Discover our selection of high-quality stepper motors now and find the right model for your project. The detailed product descriptions provide you with all the important information on technical specifications and compatibility. If you have any questions or requests, we will be happy to advise you!