Beschreibung
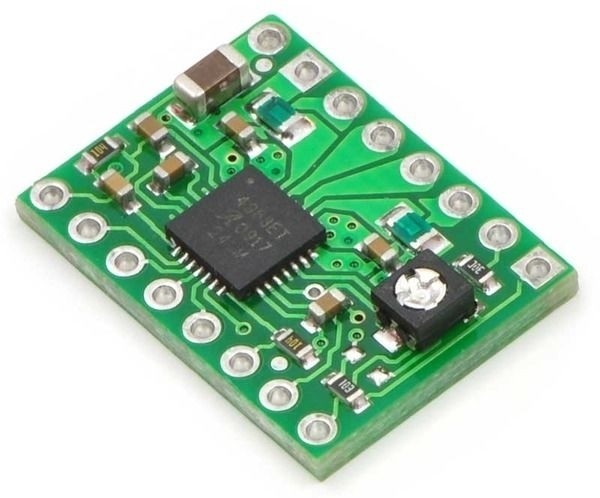
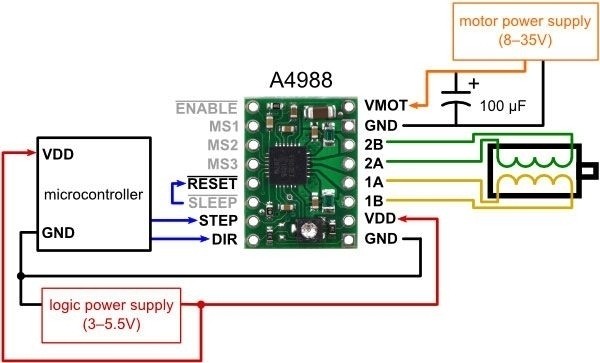
Pololu 1182 Breakout-Board für den bipolaren Mikroschritt-Schrittmotortreiber A4988 von Allegro mit einstellbarer Strombegrenzung, Überstrom- und Übertemperaturschutz sowie fünf verschiedenen Mikroschritt-Auflösungen (bis zu 1/16-Schritt).
Arbeitet mit 8 V bis 35 V und kann ohne Kühlkörper oder Belüftung bis zu ca. 1 A pro Phase liefern (bei ausreichender zusätzlicher Kühlung sind 2 A pro Spule möglich).
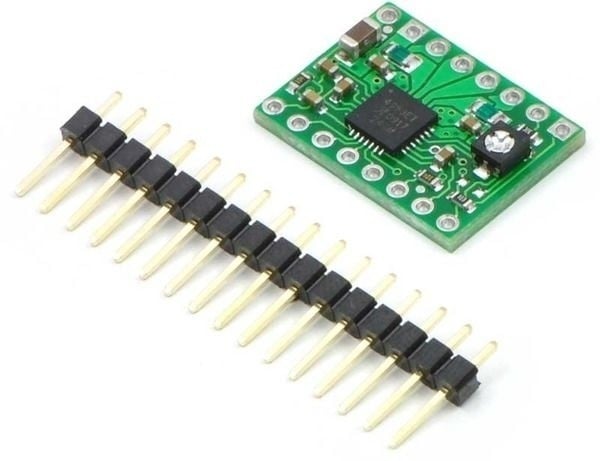
Wird mit 0,1" Stiftleisten geliefert, die jedoch nicht verlötet sind.
Spezifikationen:
- Minimale Betriebsspannung: 8 V
- Maximale Betriebsspannung: 35 V
- Dauerstrom pro Phase: 1 A
- Maximaler Strom pro Phase: 2 A
- Minimale Logikspannung: 3 V
- Maximale Logikspannung: 5,5 V
- Mikroschritt-Auflösungen: voll, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 und 1/16
- Verpolungsschutz: Nein
- Header-Pins gelötet: Nein
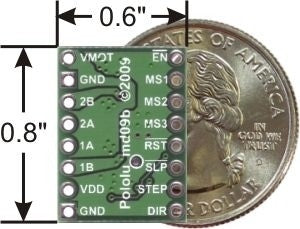
- Größe: 1,524 cm x 2,032 cm
- Gewicht: 1,3 g
Links:
Verschlüsselte Zahlung
Ihre Zahlungsinformationen werden sicher verarbeitet. Wir speichern keine Kreditkartendaten und haben auch keinen Zugang zu Ihren Kreditkartendaten.
Zolltarifnummer:
Herkunftsland:
Das hängt davon ab, wo Sie sich befinden. Nach Übergabe der Bestellung an UPS beträgt die Lieferzeit in Deutschland ca. 2-3 Tage, innerhalb Europas ca. 1 Woche.
Wir versenden unsere Artikel mit unserem Versandpartner UPS.
Wenn wir Ihre Frage noch nicht beantwortet haben, können Sie uns kontaktieren, und wir werden uns so schnell wie möglich bei Ihnen melden.